DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT CELLS AND ANIMAL CELLS:
Plant Cells:
- Cellulose cell wall present
- Pits and plasmodesmata present in the cell wall
- Plastids present
- Tonoplast present around vacuole
- Lysosomoe not normally present
Animal Cells:
- Cell wall absent, only a membrane present
- No pits and plasmodesmata present
- Plastids Absent
- Tonoplast absent
- Lysosome almost always present
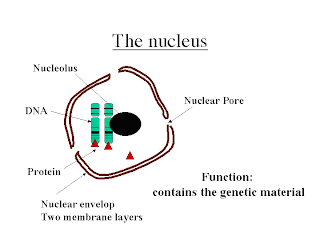
NUCLEUS
structures and functions:
Main function : it controls the cell's activities as it contains the genetic (hereditary) information in the form of DNA.
Nucleolus - a conspicuous rounded structure within the nucleus, it involves in manufacture of ribosomal RNA
Nuclear membrane - it is also called nuclear envelope which is composed of two membranes.
Nuclear pores - it allows the exchange of material between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Nucleoplasm - a gel like matrix which contains chromatin, chromosomes, one or more nucleoli(plural)/nucleolus(singular) and also a variety of chemical substances.
chromatin - it is composed mainly of coils of DNA bound to basic proteins called histones.
Other functions of nucleus:
CYTOPLASM
It consists of an aqueous ground substance containing a variesty of cell organelles and other inclusions.
Cytosol:
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
It is the main intracellular component of the cell's membrane which consists of a series of flattened cavities called cisternae(plural) / cisterna(singular)
Two types of endoplasmic reticulum:
functions:
structures and functions:
Main function : it controls the cell's activities as it contains the genetic (hereditary) information in the form of DNA.
Nucleolus - a conspicuous rounded structure within the nucleus, it involves in manufacture of ribosomal RNA
Nuclear membrane - it is also called nuclear envelope which is composed of two membranes.
Nuclear pores - it allows the exchange of material between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Nucleoplasm - a gel like matrix which contains chromatin, chromosomes, one or more nucleoli(plural)/nucleolus(singular) and also a variety of chemical substances.
chromatin - it is composed mainly of coils of DNA bound to basic proteins called histones.
Other functions of nucleus:
- to carry instruction for the synthesis of proteins in the nuclear DNA.
- to be involved in the production of ribosomes and RNA
- it involves in cell division as well
It consists of an aqueous ground substance containing a variesty of cell organelles and other inclusions.
Cytosol:
- the soluble part of the cytoplasm
- located between the cell oragnelles
- contains a system of microfilaments
- transparents and structureless when it is observed by electron microscope
- containing about 90% of water
It is the main intracellular component of the cell's membrane which consists of a series of flattened cavities called cisternae(plural) / cisterna(singular)
Two types of endoplasmic reticulum:
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum - encrusted with small particles called ribosomes
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum - doesn't encrust with any ribosomes
- Providing a large surface area for chemical reactions
- Produsing proteins ( rough ER)
- Producing lipids and steroids (smooth ER)
- collecting and storing synthesized material